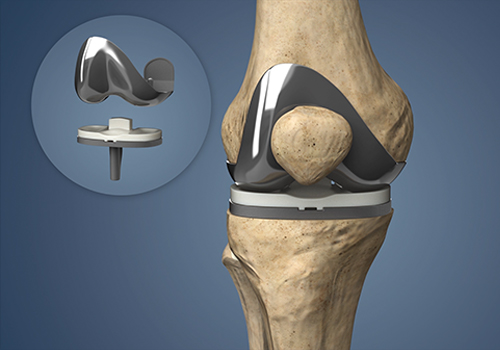
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery, a common orthopedic procedure, involves replacing damaged or worn-out knee joints with artificial implants. The surgery is typically recommended for individuals with severe arthritis, joint degeneration, or injuries causing significant pain and impaired mobility. During the procedure, the damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with prosthetic components. This surgery aims to alleviate pain, restore joint function, and improve overall quality of life. Patients undergo a thorough pre-operative evaluation to determine candidacy, and the surgery itself is performed under anesthesia. Recovery involves post-operative care, physical therapy, and gradual return to normal activities. Knee replacement has a high success rate, providing long-lasting relief for many individuals. While risks and complications exist, advancements in surgical techniques and prosthetic materials contribute to improved outcomes. Consultation with a qualified orthopedic surgeon helps determine the most suitable approach for individual cases.
Types of Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement
- Customized Implants: Tailored to individual anatomy, personalized implants enhance stability, comfort, and overall joint performance.
- Minimally Invasive Approaches: Utilizing minimally invasive methods when applicable, surgeons aim to reduce recovery time, minimize scarring, and promote faster healing.
- Pain Management Protocols: Comprehensive pain management strategies are integrated to ensure patient comfort during and after surgery, enhancing the overall recovery experience.
- Rapid Rehabilitation Programs: Structured rehabilitation plans and physical therapy facilitate early mobilization, fostering quicker recovery and improved joint functionality.
- Multidisciplinary Care Team: A collaborative approach involving orthopedic surgeons, physiotherapists, and other healthcare professionals ensures comprehensive pre-operative assessment and post-operative care.
- Cutting-edge Technology: Incorporation of state-of-the-art technologies, such as computer-assisted navigation, enhances surgical precision and improves implant alignment.
- Patient Education and Support: Informative pre-operative consultations and ongoing post-operative guidance empower patients, promoting active participation in their recovery journey.
- Proactive Infection Control Measures: Stringent infection prevention protocols are implemented to minimize the risk of post-operative infections and enhance patient safety.
- Long-term Follow-up Care: A commitment to long-term follow-up care ensures ongoing monitoring, addressing any potential issues, and promoting sustained joint health and function.These key features collectively contribute to the success and effectiveness of Total Knee Replacement surgery, providing patients with a renewed quality of life.
These key features collectively contribute to the success and effectiveness of Total Knee Replacement surgery, providing patients with a renewed quality of life.
Partial Knee Replacement
A partial knee replacement, or unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure replacing only a damaged knee compartment with an artificial implant. It's suitable for localized arthritis. Benefits include a smaller incision, faster recovery, and a more natural feel. Physical therapy is crucial for rehabilitation. While not suitable for all cases, it offers relief for the right candidates, with longevity varying. Consultation with an orthopedic surgeon is essential for personalized advice.
Common Knee Injuries And Conditions
Because the knee joint is a weight-bearing joint, it is prone to various injuries and diseases. The most common knee injuries are:
- ACL injury (anterior cruciate ligament)
- PCL injury (Posterior cruciate ligament)
- Collateral ligament injury
- Meniscal tears
- Fracture & Dislocation
Why it's done
The most common reason for knee replacement surgery is to ease pain caused by arthritis. People who need knee replacement surgery usually have problems walking, climbing stairs and getting up out of chairs.
If only one part of the knee is damaged, surgeons often can replace just that part. If the entire joint needs to be replaced, the ends of the thighbone and shinbone are reshaped and the entire joint resurfaced. These bones are hard tubes that contain a soft center. The ends of the artificial parts are inserted into the softer central part of the bones.
Ligaments are bands of tissue that help hold joints together. If the knee's ligaments aren't strong enough to hold the joint together by themselves, the surgeon may choose implants that can be connected so they can't come apart.
Risks
Knee replacement surgery, like any surgery, carries risks. They include:
- Blood clots: Surgeons typically recommend blood-thinning medications to prevent this risk. The most common location for blood clots is in the leg. But they can travel to the lungs and become deadly.
- Nerve damage: Nerves in the area where the implant is placed can be injured. Nerve damage can cause numbness, weakness and pain.
- Infection: Infection can occur at the incision site or in the deeper tissue. Surgery is sometimes needed to treat an infection.
Symptoms
When knee joint is injured, the following symptoms are experienced.
- Locking of the knee (घुटने का अटकना)
- Knee instability (घटने में लचक आना)
- Heat
- Redness
- Tenderness
- Difficulty bending the knee.
- Problems weight-bearing.
- Clicking or popping sounds.
Instant Treatment After Knee Replacement Surgery
Go after the RICE procedure to relieve knee pain.
- After knee replacement surgery, early mobility is crucial—engage in prescribed exercises and gentle movements to prevent stiffness.
- Apply ice to the surgical site to reduce swelling and manage pain, following the recommended schedule provided by your healthcare team.
- Strictly adhere to prescribed medications and follow-up appointments for optimal pain management and postoperative care.
- Keep the incision area clean and dry, following proper hygiene practices, to minimize the risk of infection and promote a smooth recovery process.